ETF 期貨產品對未來加密貨幣市場的影響
本文探討 ETF 期貨產品對市場的影響,涵蓋其核心特點、投資者需關注的關鍵要點、潛在風險以及未來發展趨勢。我們將分析期貨 ETF 如何影響市場流動性和價格波動,投資者在參與時需注意的費用、展期成本及監管因素,並展望其在機構投資、市場成熟度及監管環境變化中的角色。概述
近年來,隨著加密貨幣市場的迅速發展,傳統金融工具逐步融入這一新興領域,其中交易所交易基金(ETF)及其衍生品——期貨產品的推出尤為引人注目。2024年11月,貝萊德(BlackRock)的iShares Bitcoin Trust(IBIT)期貨產品正式上線,這一事件不僅標誌著加密貨幣與傳統金融體系進一步融合,也成為比特幣價格在2024年11月底連續衝擊歷史新高提供了重要推動力。
本文將從期貨交易的角度,深入分析ETF期貨產品對比特幣價格及未來加密貨幣市場的影響,並通過與其他資產期貨產品的對比,探討其潛在的長期意義。
加密貨幣期貨 ETF 發展史
早期探索(2013-2017):加密衍生品從無到有,期貨合約奠定基礎,受 CFTC 監管推動。
期貨 ETF 突破(2018-2021):SEC 逐步接受基於期貨的 ETF,機構參與度提升。
現貨與多元化(2022-2024):現貨 ETF 獲批標誌市場逐步成熟,以太坊 ETF 拓展衍生品邊界。

主流加密 ETF 期貨
截至2025年3月27日,市場上主流的加密貨幣ETF期貨產品主要集中在比特幣(Bitcoin)和以太坊(Ethereum)兩大加密貨幣上。
這些產品通常由知名資產管理公司推出,並在受監管的交易所(如芝加哥商品交易所CME)上交易。以下是一些當前市場上具有代表性的主流加密貨幣ETF期貨產品,重點介紹其特點和發行機構:

產品特點
1. ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO)
首隻比特幣期貨ETF:BITO 是美國市場首個獲批的比特幣期貨 ETF,提供比特幣期貨敞口,而非直接持有比特幣。
基於 CME 比特幣期貨:該 ETF 投資於芝加哥商品交易所(CME)的比特幣期貨合約,並採用現金結算方式。
受 SEC 監管:相比直接投資比特幣,BITO 作為受 SEC 監管的 ETF,適用於傳統投資賬戶,如退休賬戶(401k/IRA)。
高流動性:作為市場上交易最活躍的加密貨幣期貨 ETF 之一,BITO 具備較高的市場流動性。
費用較高:管理費為 0.95%,相比現貨比特幣 ETF 具有一定成本劣勢。

來源:https://www.proshares.com/our-etfs/strategic/bito
2. iShares Bitcoin Trust Futures (IBIT Futures)
貝萊德推出的比特幣期貨ETF:由全球最大資產管理公司 貝萊德(BlackRock) 發行,具有強大的品牌認可度和機構信賴度。
投資於 CME 比特幣期貨:ETF 持有 芝加哥商品交易所(CME) 上市的比特幣期貨合約,而非直接持有比特幣。採用 現金結算,規避比特幣託管及監管風險。
受 SEC 監管,合規性強:作為受 美國證券交易委員會(SEC) 監管的金融產品,適用於 機構和合規投資賬戶(如 401k/IRA)。
高流動性,機構友好:由於貝萊德的強大市場影響力,該 ETF 預計流動性高,適合大規模機構交易。
2024年11月將啟動 期權交易,進一步增強市場流動性,為投資者提供更多交易策略選擇。
較低的管理費用:預計 費用比率低於 1%,相比其他比特幣期貨 ETF 具有更低的成本優勢。

來源:https://www.ishares.com/us/products/333011/ishares-bitcoin-trust-etf
3. ProShares Ether Strategy ETF (EETH)
基於 CME 以太坊期貨合約:EETH 主要投資於 芝加哥商品交易所(CME) 上市的 以太坊期貨,而非直接持有 ETH 現貨。採用 現金結算模式,避免了直接持有加密資產的合規風險。
ProShares 發行:由 ProShares 發行,該公司是全球最大的槓桿與反向 ETF 提供商之一,並推出了全球首隻比特幣期貨 ETF(BITO)。ProShares 在加密期貨 ETF 方面具備豐富經驗。
受 SEC 監管,合規性強:作為 美國證券交易委員會(SEC) 批准的 以太坊期貨 ETF,EETH 適用於 機構和合規投資賬戶(如 401k/IRA)。
2023年10月2日推出:EETH 於 2023年10月2日 在美國市場正式交易,屬於首批以太坊期貨 ETF 之一。
EETH 的 管理費用比率為 0.95%,與 ProShares 的比特幣期貨 ETF(BITO)相同,略高於部分競品(如 VanEck 的 EFUT 0.66%)。

來源:https://www.proshares.com/our-etfs/strategic/eeth
4. VanEck Ethereum Strategy ETF (EFUT)
基於 CME 以太坊期貨合約:EFUT 投資於 芝加哥商品交易所(CME) 上的 以太坊期貨合約,而非直接持有以太坊現貨。採用 現金結算,避免了直接持有加密資產的合規問題和託管風險。
C-Corp 結構與稅收優化:EFUT 使用 C-Corp 結構,這一結構在美國投資中有稅務優化優勢。這種結構有助於避免基金的部分稅務負擔,提升投資者的淨回報,特別適合稅務規劃的投資者。
受 SEC 監管,合規性強:EFUT 作為 SEC 批准的期貨ETF,確保了高度合規,適用於各種機構和個人投資者。該 ETF 通過受監管的期貨市場提供了合法的以太坊市場敞口。
較低費用比率 0.66%:與市場上其他加密貨幣期貨 ETF 相比,EFUT 提供了 較低的管理費用比率 0.66%,使其對投資者更具吸引力。相比 ProShares Ether Strategy ETF(EETH) 的 0.95% 費用,EFUT 更具成本優勢。

來源:https://www.vaneck.com/us/en/investments/ethereum-etf-ethv/overview/
5. Bitwise Bitcoin and Ether Equal Weight Strategy ETF
多元化敞口,等權重配置:Bitwise Bitcoin and Ether Equal Weight Strategy ETF 投資於 比特幣(BTC) 和 以太坊(ETH),採用 等權重或市值加權 策略。該 ETF 提供對這兩大加密貨幣的 多元化敞口,使投資者能夠同時受益於比特幣和以太坊的市場表現。
基於 CME 期貨合約:ETF 投資於 CME 上的比特幣和以太坊期貨合約,而非直接持有現貨加密資產。現金結算,降低了加密貨幣託管和監管的合規風險。
較小的資產規模(AUM):與一些大型加密貨幣 ETF 相比,Bitwise Bitcoin and Ether Equal Weight Strategy ETF 的 資產規模較小,通常在 數千萬美元 級別。這種小規模可能意味著較高的 波動性和風險,但也為投資者提供了潛在的高收益機會。
費用比率:該 ETF 的 費用比率 在 0.85%-1% 之間,適中,較低於一些更高費用的加密貨幣期貨 ETF,如 Valkyrie Bitcoin and Ether Strategy ETF 的 1.24%。適合尋求成本較低的多元化加密貨幣敞口的投資者。
6. Valkyrie Bitcoin and Ether Strategy ETF (BTF)
比特幣和以太坊的靈活配置:Valkyrie Bitcoin and Ether Strategy ETF (BTF) 投資於 比特幣(BTC) 和 以太坊(ETH) 期貨合約。
與其他 ETF 不同,BTF 採用 動態調整比例,使其能夠根據市場走勢調整比特幣和以太坊的配置比例,提供 靈活的資產配置。
基於 CME 期貨合約:該 ETF 投資於 CME 上的比特幣和以太坊期貨合約,而非直接持有現貨加密資產。採用 現金結算,有助於降低託管風險和合規問題。
資產規模(AUM):BTF 的資產規模 介於數千萬至1億美元之間,較小,但為尋求靈活配置的投資者提供了多樣化選擇。相較於一些規模更大的加密貨幣 ETF,BTF 在靈活配置上提供了更多優勢。
費用比率 1.24%:BTF 的費用比率為 1.24%,相較於市場上其他加密貨幣 ETF 較高。儘管費用較高,但其靈活的配置策略和投資組合調整的優勢,可能吸引那些尋求動態資產配置的投資者。

來源:https://www.nasdaq.com/market-activity/etf/btf
與其他資產期貨產品的對比
為了更全面理解ETF期貨產品對加密貨幣市場的影響,我們可以參考其他資產類別引入期貨後的表現,例如黃金和原油。

1.黃金期貨的經驗
黃金期貨於1974年在美國推出,隨後成為全球黃金市場的重要組成部分。研究表明,黃金期貨的引入顯著降低了現貨市場的波動性,並提升了價格透明度。
類似地,IBIT期貨的上線可能為比特幣市場帶來類似效應——通過吸引機構資金和完善價格發現機制,逐步削弱其“高波動性”標籤。然而,與黃金不同,比特幣的供應固定且缺乏實物使用價值,其價格更多依賴市場情緒,因此期貨的影響可能更偏向短期放大而非長期穩定。

來源:https://etfdb.com/etfs/commodity/gold/
2.原油期貨的教訓
原油期貨市場的發展則揭示了槓桿交易的另一面。1983年WTI原油期貨推出後,市場流動性大幅提升,但也因投機資金的介入而加劇了價格波動。
例如,2008年油價暴漲暴跌的部分原因便與期貨市場的過度槓桿有關。對比特幣而言,IBIT期貨的槓桿特性可能在未來牛市中推動價格快速上漲,但也可能在熊市中引發連鎖清算,加大市場風險。

來源:https://futures.tradingcharts.com/historical/CO/1983/3/barchart.html
3.加密貨幣的獨特性
與傳統資產相比,比特幣市場的參與者結構更為分散,且散戶佔比更高。IBIT期貨的上線雖然吸引了機構入場,但散戶情緒仍可能通過現貨市場反作用於期貨價格。這種雙向互動使得比特幣期貨的影響更加複雜,可能呈現出比黃金或原油更強的短期波動特徵。
ETF期貨對未來市場的影響
ETF期貨產品(如比特幣和以太坊期貨ETF)對未來市場的影響是一個多維度的話題,涉及價格機制、市場結構、投資者行為以及監管環境等多個方面。以下從短期、中期和長期視角,結合現有趨勢和潛在發展,分析其對未來加密貨幣市場的影響。
短期影響(1-2年)
1.價格波動放大
ETF期貨的槓桿特性(如10倍槓桿)和投機資金將放大價格波動。例如,2021年BITO推出後,比特幣短期內上漲超20%,但隨後因清算回調。未來類似產品(如IBIT Futures)可能加劇這一效應,尤其在牛市初期或關鍵事件(如監管利好)時。
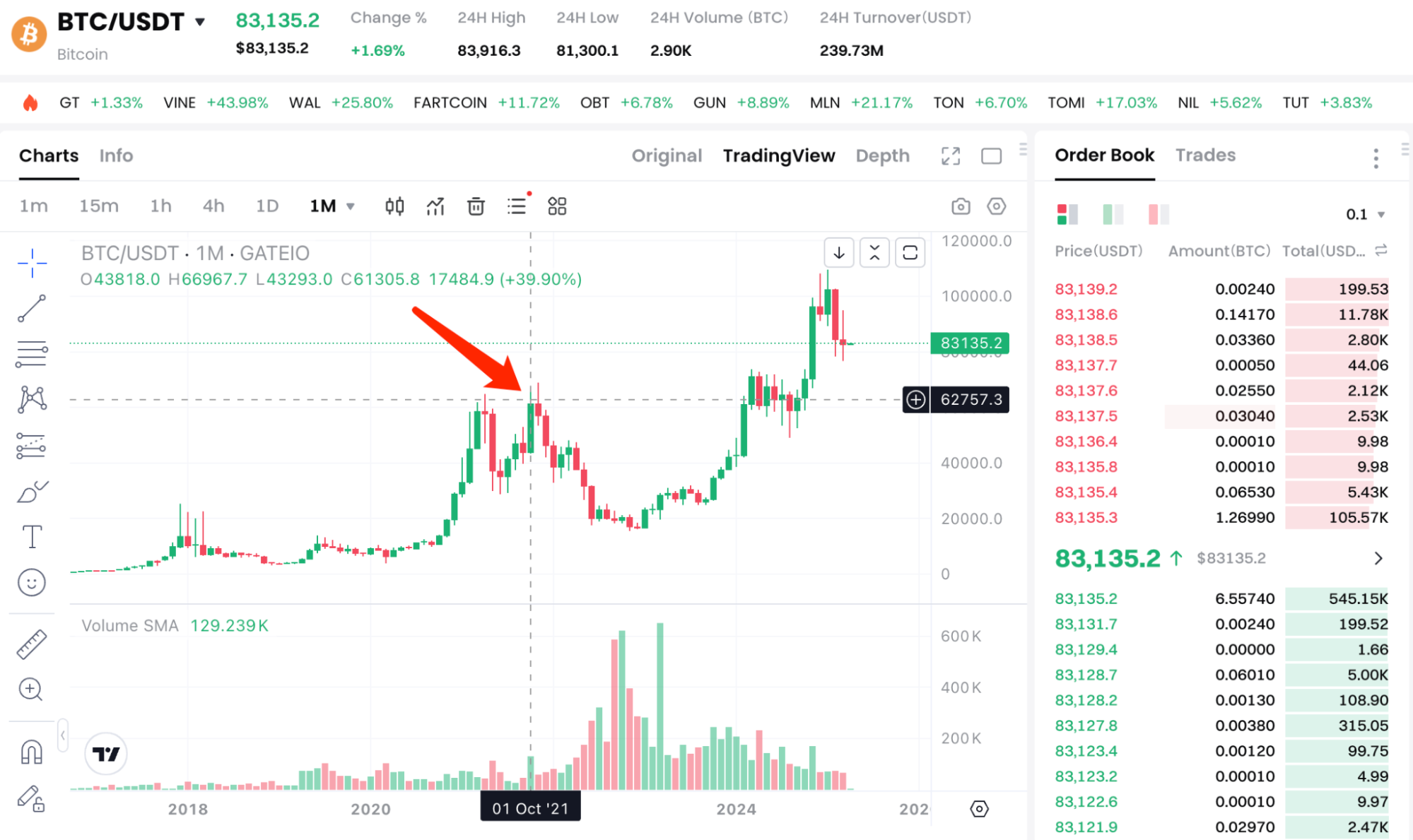
來源:https://www.Gate.com/trade/BTC_USDT
2.流動性提升
期貨ETF吸引機構和零售資金,增加市場交易量。例如,BITO日均交易額超1億美元,顯著提升CME比特幣期貨流動性。短期內,這將提高市場效率,但也可能因投機交易而推高波動性。
3.投機情緒主導
槓桿工具吸引短期投機者,市場可能出現“追漲殺跌”。2024年11月比特幣突破10萬美元,部分歸因於期貨市場的多頭情緒。短期內,投機將主導價格走勢,增加泡沫化風險。
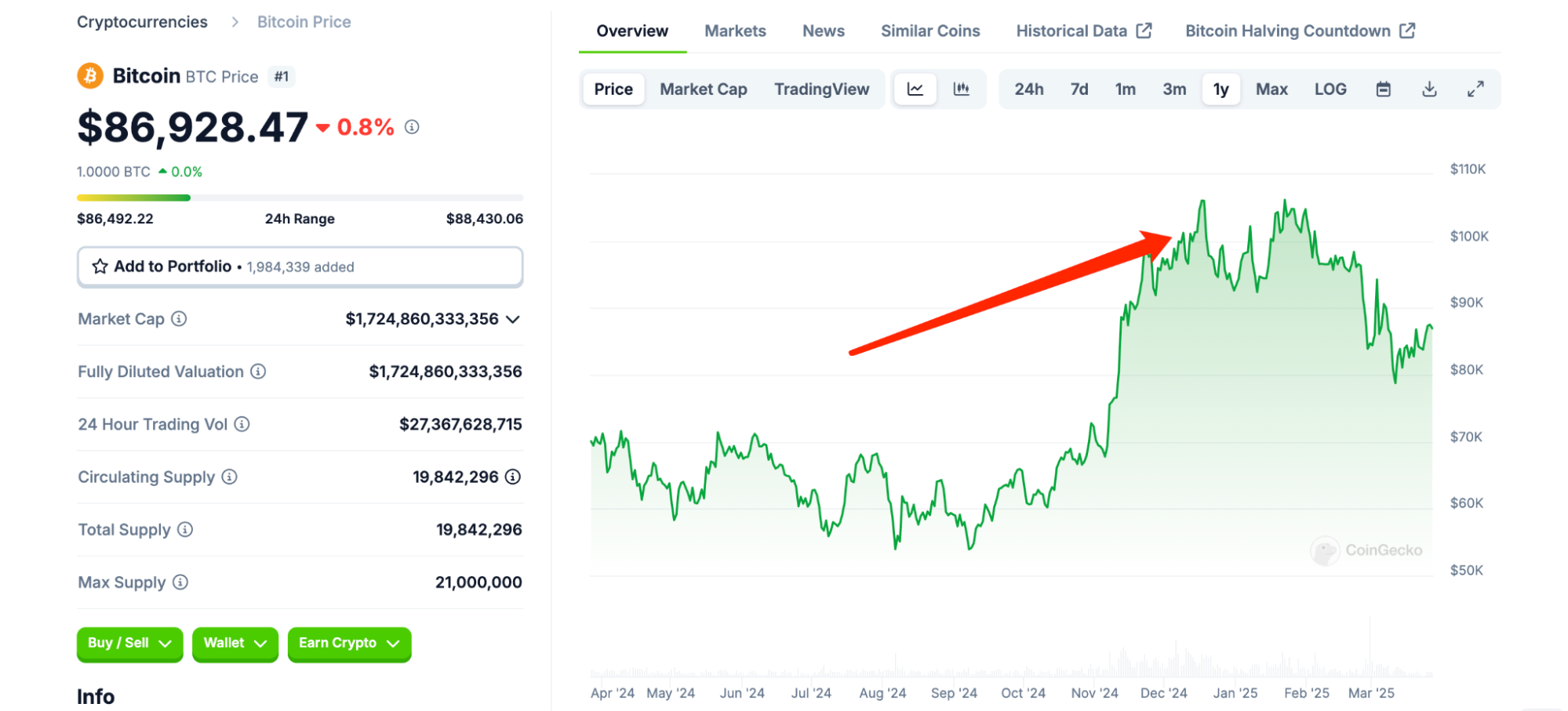
來源:https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/bitcoin
中期影響(3-5年)
1.市場成熟與機構化
期貨ETF作為橋樑,吸引機構資金入場。例如,貝萊德的IBIT已積累超500億美元資產,其期貨版本可能進一步推動機構參與。中期內,市場將從散戶主導轉向機構主導,波動性逐步下降,類似傳統資產。
2.價格發現優化
期貨市場的套利交易(如現貨與期貨價差)將完善價格發現機制。例如,CME期貨已使比特幣價格更透明。未來3-5年,價格將更穩定地反映供需,而非單純依賴情緒。
3.產品多元化
成功案例(如BITO)將激勵更多衍生品推出,如以太坊、Solana期貨ETF或混合型產品(如BTF)。中期內,投資者可通過多空策略參與,市場生態更豐富,風險分散。
長期影響(5-10年及以上)
1.主流化與合法化
期貨ETF將推動加密貨幣融入傳統金融,類似黃金ETF的普及效應。若監管支持,長期內比特幣和以太坊可能成為標配資產,市場規模或從當前2-3萬億美元升至10萬億美元。
2.波動性趨於穩定
隨著市場深度增加和參與者多樣化,波動性將降低。例如,比特幣年化波動率可能從50%-80%降至20%-30%,接近黃金或大宗商品,吸引保守型資本。
3.競爭與替代效應
現貨ETF(如FBTC資產超1120億美元)因低成本可能逐漸取代期貨ETF的主導地位。長期內,期貨ETF或退居投機和對衝工具,市場重心轉向現貨持有。
投資者參與需要注意什麼
投資者參與期貨ETF時需關注高波動性和槓桿效應,這可能放大風險。期貨ETF的費用較高,包括管理費和展期成本,可能影響回報。
適合短期投機或對衝,而長期投資者應考慮現貨ETF。此外,投資者應關注市場流動性、監管政策和宏觀經濟因素,制定清晰的策略並控制風險。

風險
ETF期貨產品(如比特幣或以太坊期貨ETF)雖然為投資者提供了便捷的加密貨幣敞口,但其獨特的金融結構和市場特性也帶來了多種風險。以下是ETF期貨產品存在的核心風險,涵蓋市場、操作、結構和外部因素等方面:
1. 市場風險
高波動性: 加密貨幣市場本身波動劇烈,期貨ETF通過槓桿效應進一步放大價格波動。例如,比特幣單日漲跌10%可能導致期貨ETF淨值更大變化。
投機驅動: 期貨市場易受投機情緒影響,短期內可能出現非理性漲跌,與標的資產(比特幣、以太坊)的基本面脫節。
清算風險: 在極端行情下(如2022年加密熊市),槓桿頭寸可能被強制平倉,導致投資者損失超出預期。
案例: 2021年BITO推出後,比特幣價格一度飆升,但隨後市場回調導致部分投資者因槓桿清算而虧損。

來源:https://www.cnbc.com/2022/07/14/why-the-2022-crypto-winter-is-unlike-previous-bear-markets.html
2. 展期風險(Roll Risk)
展期成本: 期貨ETF需定期將到期合約滾動至下一期。若市場處於“正向溢價”(Contango),遠期合約價格高於現貨,滾動時需“高買低賣”,產生成本,侵蝕長期收益。
逆向溢價影響: 若市場處於“逆向溢價”(Backwardation),遠期價格低於現貨,滾動可能帶來額外收益,但這種情況較少且不可預測。
跟蹤誤差: 由於展期成本和市場波動,期貨ETF的回報可能偏離現貨價格表現。
案例: BITO在2022年Contango市場中,年度展期成本高達5%-10%,顯著拖累長期持有者的回報。
3. 槓桿風險
放大效應: 期貨合約天然帶有槓桿(如10倍或更高),少量資金可控制大額頭寸。雖然這能放大收益,但下跌時虧損同樣被放大。
保證金要求: 若市場逆向波動,經紀商可能要求追加保證金(Margin Call),未及時補足可能導致強制平倉。
系統性風險: 大規模槓桿清算可能引發連鎖反應,加劇市場下跌。
案例: 2021年比特幣期貨市場因過度槓桿化,在5月暴跌中觸發大量清算,影響相關ETF表現。
4. 流動性風險
交易量不足: 部分期貨ETF(如規模較小的EFUT)可能流動性較低,導致買賣價差擴大,交易成本上升或難以快速平倉。
市場深度問題: 在極端行情下,即使是高流動性產品(如BITO),也可能因訂單簿稀薄而出現滑點。
時間錯配: 期貨ETF按傳統股市時間交易(而非加密市場的24/7),可能錯過夜間價格波動,影響執行效率。
案例: 小型期貨ETF在2023年加密市場低迷時,日均交易量不足百萬美元,投資者退出時面臨較大價差損失。
5. 費用風險
高管理費: 期貨ETF的管理費通常高於現貨ETF(如BITO為0.95%,對比FBTC的0.25%),長期持有成本較高。
隱性成本: 除管理費外,展期成本、經紀佣金和價差也會增加實際費用,尤其在高頻交易中。
費用波動: 某些ETF可能因市場競爭調整費率,但短期內可能面臨費率不確定性。
案例: BITO投資者在2022年發現,綜合成本(管理費+展期)遠超預期,導致實際收益低於比特幣現貨漲幅。

來源:https://finimize.com/content/should-you-buy-into-the-worlds-first-bitcoin-etf
6. 監管與政策風險
監管變化: 美國SEC或CFTC可能調整對期貨ETF的監管政策(如限制槓桿比例或交易規模),影響產品運作或投資者准入。
稅收不確定性: 在某些司法管轄區,期貨ETF收益可能按短期資本利得稅計算(稅率較高),且政策可能隨時調整。
國際差異: 若投資者所在國家對加密貨幣或衍生品有限制,可能面臨交易禁令或資金凍結風險。
案例: 2021年中國全面禁止加密交易,導致部分國際投資者無法通過本地賬戶參與BITO交易。
7. 操作與技術風險
基金管理風險: ETF管理人(如ProShares、貝萊德)的操作失誤(如錯誤展期時機)可能影響基金表現。
技術故障: 交易所或經紀商平臺的技術問題(如系統宕機)可能導致無法及時交易,尤其在高波動時。
對手方風險: 雖然CME等交易所受監管,但期貨合約仍涉及對手方信用風險,若清算機構出現問題,可能影響結算。
案例: 2020年CME比特幣期貨因技術問題短暫暫停交易,影響相關ETF的流動性。

來源:https://www.inc.com/associated-press/trading-is-halted-on-nyse-because-of-technical-outage.html
8. 宏觀經濟與外部風險
利率波動: 美聯儲加息會提高期貨市場的資金成本,降低高風險資產(如比特幣)的吸引力,間接影響ETF表現。
市場情緒: 加密貨幣價格易受外部事件驅動(如黑客攻擊、名人言論),期貨ETF可能放大這些波動。
競爭壓力: 隨著現貨ETF(如IBIT、FBTC)普及,期貨ETF可能因成本劣勢失去吸引力,導致資金流出。
案例: 2022年美聯儲加息週期中,比特幣價格承壓,BITO淨值同步下跌,部分投資者轉向低成本現貨ETF。
未來展望
展望未來,ETF期貨產品可能從以下幾個方面重塑加密貨幣市場:
1.主流化與機構化
IBIT期貨的成功預示著加密貨幣將進一步融入主流金融體系。更多機構投資者的參與不僅提升市場深度,也可能推動監管框架的完善。這將吸引更多傳統資本進入加密領域,擴大市場規模。
2.多元化產品生態
貝萊德的先行示範效應可能激勵其他資產管理公司推出類似產品。例如,以太坊、Solana等其他加密貨幣的期貨ETF或將陸續上線,形成多元化的加密衍生品生態。這種趨勢將為投資者提供更多選擇,同時分散單一資產的風險。
3.價格波動的新常態
短期內,期貨產品的槓桿效應可能加劇比特幣價格的波動,尤其在市場情緒極端時。然而,隨著市場成熟度和參與者多樣性的提升,長期波動性有望逐步下降,比特幣可能逐漸向傳統資產靠攏。
結語
貝萊德 IBIT 期貨產品的上線無疑是加密貨幣市場的重要里程碑。從期貨交易的角度看,它通過提升流動性、引入槓桿和完善風險管理,推動了比特幣在 11 月底創下新高。與黃金、原油等傳統資產的期貨發展相比,IBIT期貨既展現了相似的市場深化效應,也因加密貨幣的獨特性而呈現出更強的短期放大效應。
未來,隨著ETF期貨產品的普及,加密貨幣市場有望邁向更成熟、多元化的新階段。然而,投資者需警惕槓桿交易帶來的雙向風險,在參與這一新興市場時保持審慎態度。
相關文章

區塊鏈盈利能力和發行 - 重要嗎?

比特幣年第二章

Notcoin & UXLINK:鏈上數據比較

FIT21“21世紀金融創新與技術法案”的詳細分析
Solv協定:集中式去中心化金融趨勢下的資產管理新範式